Offline Sorter
Offline Sorter™ (OFS) is the most recognized and trusted offline spike sorting software in the industry today, with more than 1,700 publications specifically citing the use of OFS as part of their methods. OFS accepts file types from many data acquisition companies and software programs listed in the specifications table in the Technical Specs tab below – and now reads .PL2 files.
**Visit the Getting Started with Offline Sorter page for New video tutorials **
**Free Upgrades within Versions**
Latest Software Downloads
Offline Sorter v4.7.1 – Windows 10 (64 bit)
Offline Sorter v4.7.1- Windows 7, 10 (32 bit)
Offline Sorter v3.3.5 – Windows 7, 8, 10 (64 bit)
Offline Sorter v3.3.6.1 – Windows 7, 8, 10 (32 bit)
Offline Sorter v3.3.3 – Windows XP (64 bit)
Offline Sorter v3.3.3 – Windows XP (32 bit)
Offline Sorter v2.8.8 – Windows XP
NEW OFS v4 is a powerful, easy-to-use tool for viewing and classifying action potential waveforms (spikes) previously collected from single electrodes, stereotrodes and tetrodes. Version 4 is loaded with new sophisticated algorithms and functionality including the ability to analyze overlapping waveforms, perform signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) computations, apply high-cut filtering to continuous channels and exploit digital referencing. OFS version 4 is further packed with additional new functionality including but not limited to the ability to load multiple PL2™ files simultaneously; new L-Ratio and Isolation Distance sort quality metrics; support for Band and Line sorting methods; ability to name and manipulate Time Segments and save as NeuroExplorer® files; new scan modes including the ability to scan using different random initial seed clusters; support for multiple spike Sources; ability to display arbitrary combinations for continuous and spike data together for a channel in the Timeline View; the ability to use standard deviation or Median Absolute Deviation (MAD) to calculate fit or band fit tolerances and much more.
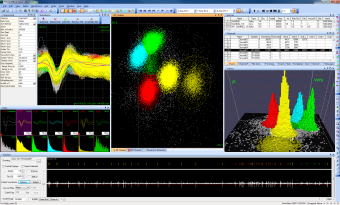
Spikes are displayed as points in either two-dimensional (2D) or three-dimensional (3D) feature space, where a variety of manual, semi-automated or fully-automated clustering techniques can be applied to classify (sort) the spikes. Our spike sorting software can also perform spike extraction on continuously recorded neural data using a variety of different thresholding methods. OFS allows sorting verification through a variety of displays and can calculate cluster separation statistics and sort quality metrics. The sorted spikes can be exported in several formats for subsequent analysis.
The parameter space for several fully automatic spike sorting algorithms can be systematically scanned with graphs displaying the sort quality metric as a function of the varied parameters. The results of the automated scanning through sorting parameter space can be saved in a SCAN file. Combined with new batch mode commands, this process allows the running of various sorting algorithms, which is followed by rapid manual viewing of different sort outcomes and selection of the appropriate sort for each channel.
OFS also contains new time-segmented views of the waveforms with cluster vs. time and sort quality vs. time views that show how the waveforms change and evolve. Multiple methods for spike detection in continuously digitized data files can be used, including voltage threshold, signal energy and nonlinear energy. Additionally, stereotrode and tetrode spike detection is supported. A low-cut filter may be applied to the continuous data prior to spike extraction.
Powerful Waveform Viewing and Sorting
- NEW Overlapping waveform analysis
- NEW Ability to display arbitrary (compatible) combinations of continuous and spike data for a channel together in the Timeline View which replaces the need to associate channels during loading of .PLX files or during channel remapping
- NEW Support for multiple spike Sources
- Manual cluster selection in 3D feature space using principal component projections, voltage slices in time, or more than 20 other waveform features such as peak, valley, full-width at half maximum, etc.
- Box sorting as a pair of time-level windows
- Waveform selection in time-voltage space
- Template matching algorithm
- Tetrode and Stereotrode waveform extraction and sorting using any method
- Unit cross-correlograms and ISI plots
- Waveform density plots in 2D or 3D in any feature space
- Waveform alignment
- Interval invalidation and artifact removal
- Raster displays of spikes and continuous data
- Printable Sorting Summary View with export to PowerPoint®
- Waveform features and statistics can be easily exported to MATLAB®, Excel® or text file
- Export of sorted data to NeuroExplorer®
- Save and recall particular sorting instances for a selected channel (useful for comparisons)
Time Segmentation, Adaptive Sorting Methods, and Time-Dependent Analysis
- NEW Time Segments can be named and individually colored and toggled on/off, and can be saved/restored as NeuroExplorer Intervals
- NEW Interval Selection tool can create Time Segments
- NEW Ability to load multiple .PL2 files simultaneously
- Divide each file into time segments and view and sort waveforms from each time segment separately
- Clusters vs. Time View to show how clusters evolve as a function of time
- Sort Quality View vs. Time Segment Graph View to display how the sort quality changes through the file
- Adaptive template sorting, with the templates changing over time to follow the waveform as it evolves
- Template vs. Time View to display how the template adapted through the file
Semi-Automatic and Automatic Sorting
- NEW Added L-Ratio and Isolation Distance sort quality metrics
- NEW Support for Lines and Bands in Change Sort Method
- NEW Scan modes, including ability to scan using different random initial seed clusters
- NEW Can use standard deviation or MAD to calculate fit tolerances or band fit tolerances
- Enhanced automatic sorting methods with systematic scanning through parameter space and graphs displaying the sort quality metric as a function of the parameters that were varied; select the best sorting according to a selected sort quality metric
- Automatic sort scan results for each channel can be saved to and loaded from .SCAN files. Together with the new batch mode scan commands, this process will allow the running of certain sorting scans overnight, followed by manual reviewing and selection of the most appropriate sort for each channel
- Automatic cluster selection in feature space using Valley Seeking or T-Distribution Expectation Maximization (E-M)
- Semi-automatic cluster selection in feature space using K-Means or Standard E-M
Enhanced Batch Mode Processing for Running Sorting Algorithms Overnight
- Batch mode commands for scanning through automatic sorting parameters
- Menu item to edit batch files with a user-selected editor
- Memory of previous batch file locations
- Quick Batch Reference showing all batch commands
- Menu item shows log file resulting from the latest batch run
Enhanced Continuous Data Handling and Spike Detection
- NEW Ability to apply high-cut filtering to continuous channels
- NEW Digital referencing
- NEW Signal-to-Noise ratio (SNR) computation
- NEW Threshold Scan Graph View allows examining SNR and number of spikes as a function of threshold position for continuous data
- Up-sampling of continuous signals, with linear or spline interpolation
- Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) View of continuous data
- Single and Dual Thresholds for spike detection
- Waveform detection and extraction now appropriately handles differences in voltage scales between spike waveform segments and continuous spike data
Improved User Interface, Displays, and Performance
- NEW Contents of the Sort Summary View are customizable
- Now reads .PL2 files for single channel read times up to 100s or 1000s of times faster
- Enhanced bottom Timeline View showing both continuous and waveform data simultaneously with a resizable splitter
- Mouse-over time and voltage readings in the Waveform View and Continuous Data View
- More information related to gains and voltage ranges in the Channel Parameters View and File Summary View
- Select main menu item to select the next/previous channel, unit, waveform, or time segment
- Performance enhancements for faster processing of large data files
- Available as a true 64-bit executable for faster processing of large data files
Offline Sorter is an exceptionally popular program, and its use is often followed by analysis in NeuroExplorer. All upgrades within a version are free of charge and will be accessible online upon release. If you have additional questions, a Plexon Sales Engineer is happy to discuss this or any other Plexon products with you further.
| Features | Specifications and Options | Remarks |
| File types supported | Plexon (.PL2, .PLX), NeuroExplorer® (.NEX), Alpha Omega (.MAP, .MPX), Axion Biosystems (.SPK, .RAW), Cyberkinetics/Blackrock Microsystems (.NEV, .NS5), CED Spike-2 (.SMR), DataWave (.UFF, .DAT, .CUT, .ACT), Neuralynx (.NTT, .NST, .NSE, .NCS, .NVT), MultiChannel Systems (.MCS, .MCD), Panasonic (.MED), Neuroshare (.NSN), Data Translations (.DCF), generic binary continuous data, and other formats supported via Neuroshare | |
| Spike detection methods | – Voltage Threshold – Signal Energy – Nonlinear Energy – Signed Signal Energy | |
| Spike sorting methods | – Manual methods: Boxes, Lines, Bands, Waveform Crossing and Contours – Semi-Automatic methods: Templates, K-Means and Standard E-M (Expectation – Automatic methods: Valley-Seeking, T-Distribution E-M and Scanning methods | |
| Features available for sorting | – Projections onto principal components (PCA) – Waveform heights at chosen times (“slices”) – Peak height, valley height, peak-valley difference, widths – Timestamp of the waveform – For stereotrode and tetrode data, per-electrode and ratio-between-electrodes features | |
| Views available | – Waveforms – Units – Timeline – 2D or 3D Clusters – Surface – Clusters Vs Time – Sort Quality vs Time Segment Graph – Waveform Inspection – Waveform Detection – Continuous Frequency Spectrum – ISI Histograms – Feature vs. Feature – Sorting Summary – PCA Results – Cross-Correlograms – Rasters | |
| Electrode support | Single, stereotrode and tetrode | |
| Export options | MATLAB®, Excel®, text file or NeuroExplorer | Waveform features and statistics. |
| Activation requirement | Plexon version-specific USB license key | OFS can be ordered in 1 or 2 license key options. OFS may be installed on an unlimited number of computers. However, a license key is required to operate the spike sorting software on a specific computer at the time of use. |
| Recommended system requirements: | ||
| Computer CPU | Intel Core i5 / AMD Ryzen 5 | |
| Platform | 64-bit Windows 10 | Version 4 runs on Windows 7, 8 and 10. Last Version 3 update for Windows 7, 8, and 10 is v3.3.5. Last Version 3 update for Windows XP is v3.3.3. |
| RAM | 16+ GB | |
| Graphics | Dedicated Nvidia or AMD graphics card with OpenGL support | |
| Disk | SSD or M.2 | |
| Minimum system requirements: | ||
| Computer CPU | Intel Core i3 / AMD Ryzen 3 | |
| Platform | 32 or 64-bit Windows 7/10 | Version 4 runs on Windows 7, 8 and 10. Last Version 3 update for Windows 7, 8, and 10 is v3.3.5. Last Version 3 update for Windows XP is v3.3.3. |
| RAM | 4 GB | |
| Graphics | Dedicated NVidia or AMD graphics card with OpenGL support |
Installation Packages/Upgrades
- Offline Sorter v4.7.1 – Windows 10 (64 bit) Post date February 24th, 2023
Also compatible with Windows 7
- Offline Sorter v4.7.1 – Windows 10 (32 bit) February 24th, 2023
Also compatible with Windows 7
- Offline Sorter v3.3.5 – Windows 10 (64 bit) Post date April 21, 2015
Also compatible with Windows 7 & 8
- Offline Sorter v3.3.6.1 – Windows 10 (32 bit) Post date March 23, 2021
Also compatible with Windows 7 & 8
- Offline Sorter v3.3.3 – Windows XP (64 bit) Post date September 22, 2014.
You may need to download Sentinel Driver v7.5.8 found at http://www.safenet-inc.com/support-downloads/sentinel-drivers. Last version 3 update for Windows XP.
You may need to download Sentinel Driver v7.5.8 found at http://www.safenet-inc.com/support-downloads/sentinel-drivers. Last version 3 update for Windows XP.
- Offline Sorter v2.8.8 – Windows XP Post date February 2, 2009
Manuals/User Guides
Guides and How To Papers
For Offline Sorter v2 and v3 and CinePlex Editor v3.4.1
Change Log
- Offline Sorter Change Log Post date February 24th, 2023
Technical Specs and Data Sheets
Videos
